Foreword <br>Laser injection-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) has been a research hotspot in the field of solid micro-area analysis since it was applied in the mid-to-late 1980s. This technology effectively avoids secondary pollution and possible error introduction caused by complex sample pretreatment such as acid dissolution and digestion, and truly realizes functions such as micro-loss, in-situ micro-region, and rapid injection, especially for mineral standards and trace amounts. Precious samples such as physical evidence and gemstone are of great significance. However, the elemental fractionation effect has always been an important factor restricting the development of this technology, especially when using the nanosecond laser injection system for in-situ single-point analysis of smaller beam spots (<20μm), the fractional effect of elements is very obvious. Affecting the accuracy of data analysis is difficult to use as a routine laboratory analysis method. Ø Repeat frequency: 4 Hz From Figure 3 we can see that the signal intensity of each isotope is relatively stable during data signal acquisition. At the same time, the change behaviors of the three isotopic signal intensities are relatively consistent, and the fractionation effect of the elements is small, which is consistent with the basic characteristics of zircon. Disposable Mask,Black Disposable Mask,N95 Disposable Mask,Best Disposable Mask Zhejiang Lanhine Medical Products Ltd. , https://www.lanheyiliao.com
In order to better avoid the influence of element fractionation effect, in this experiment, the in situ single-point 238 U/ 206 Pb ratio of zircon was determined by J200 femtosecond laser injection-multiple-receiving inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. It is used to explore the data accuracy of in-situ single-point analysis of zircon in a femtosecond laser injection-multiple-receiving inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with a small laser beam spot of 20 μm.
Experimental Instruments and Parameter Settings <br>This experiment was performed using the Applied Spectra, Inc. J200 343nm femtosecond laser sampling system in combination with the Neptune Plus multi-receiving inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (fs LA-MC-ICP). -MS), instrument experimental parameters are as follows:
l US Applied Spectrometry J200 343nm femtosecond laser injection system Ø femtosecond laser wavelength: 343 nm 
Ø Laser pulse maximum energy: 120μJ
Ø Sampling mode: in-situ single-point multi-pulse Ø pulse number: 190 times Ø sampling laser beam spot size: 20μm
Ø He gas flow rate: 0.52 L/min
Ø Ar gas flow rate: 1.2 L/min
l Neptune Plus multi-receiver inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer Ø Cooling gas flow: 15L/min
Ø Auxiliary gas flow: 1.0L/min
Ø RF power: 1000W
Ø Extraction voltage: 2000V
Ø 238 U sensitivity: 50mv/ppb
Ø Sampling time: 54S (collecting blank data 20S)
Ø Multi-receiver cup structure 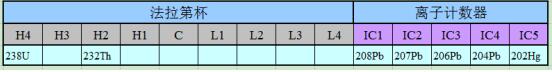
experimental method
1. Prior to testing the zircon sample, the laser conditions were first corrected and set. The NIST 610 standard sample was linearly scanned using the J200 femtosecond laser sampling system (laser pulse energy: 100%; beam spot size: 20 μm; repeat Frequency: 20HZ), adjust the instrument parameters so that the 238 U signal rises to about 3V, and the signal is stable.
2. In-situ single-point multi-pulse sampling of zircon samples under optimal laser conditions, the laser energy is 30% of the maximum value, and the sampling time is 54S (blank data acquisition 20S). When the sampling position is selected, since the zircon sample has an obvious magma oscillation ring structure inside, it avoids existence.
The cracked zircon and the core of the zircon are treated with 20um smear and the zircon with obvious ring structure is used for ablation. The sampling position is shown in Figure 1. The J200 femtosecond laser injection operation interface is shown in Figure 2: 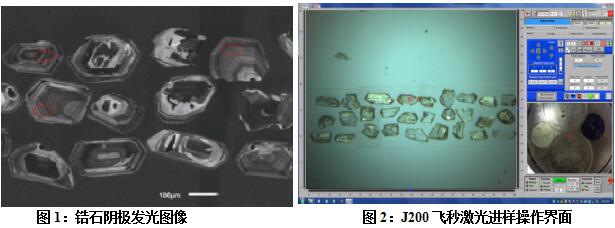
Experimental data analysis
1. MS signal strength stability and fractionation effect, as shown in Figure 3: 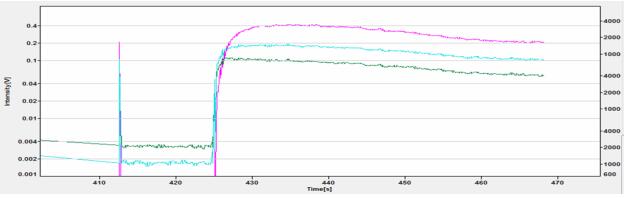
Figure 3: MS signal strength (red for 238 U, blue for 206 Pb, green for 207 Pb)
2. Isotope ratio and RSD deviation, as shown in Figure 4: 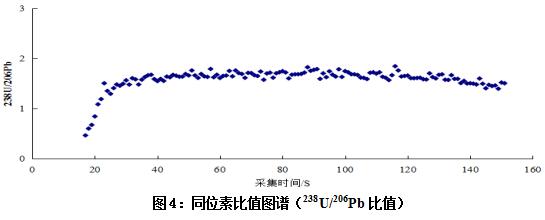
From Figure 4, we can see that the stability of 238 U/ 206 Pb ratio data is relatively good. The original data is analyzed by Excel software, and the RSD deviation of 238 U/ 206 Pb ratio in all effective acquisition time periods is about 3%. .
Conclusions <br>The elemental fractionation effect of zircon in a 20μm in-situ single-point sampling using the J200 femtosecond laser sampling system is relatively small, and the 238 U/ 206 Pb ratio data obtained by mass spectrometry is stable. It can be used as a routine laboratory method for in situ single point determination of zircon isotope ratios by laser beam spot (20 μm). In addition, the zirconium isotope ratio of tiny beam spots (below 5 μm) can be measured by the advantages of the J200 femtosecond laser sampling system.